Xiaomi primed to start deliveries of SU7 electric sports saloon

Deliveries of Xiaomi’s first electric car are due to begin this month with pricing set to be revealed on 28 March.
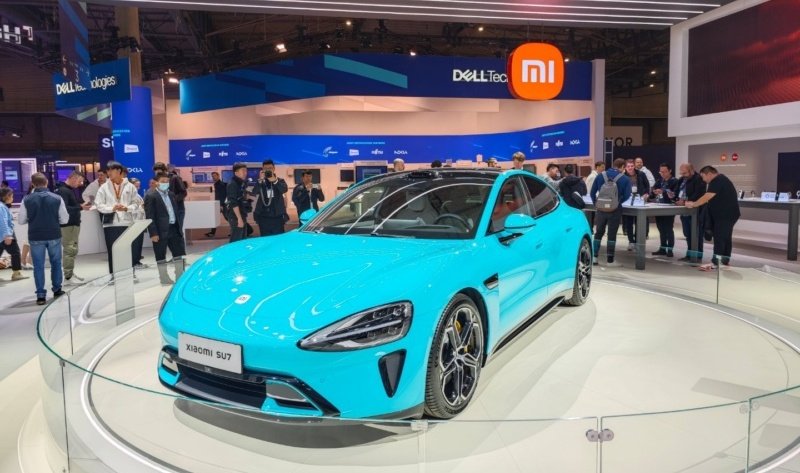
The brand’s first-ever production car, the Xiaomi SU7 is a Porsche Taycan-rivalling electric saloon which is the first among a range of new models set to launch over the next few years.
It will first be available in China, where 59 stores in 29 cities are primed to take orders, but Xiaomi has plans for global sales.
The new saloon debuted 1003 days after the Chinese consumer electronics company initially announced its plans to enter the electric car ranks in 2021 with an initial investment of RMB10 billion (£1.1 bn) and plans for a further RMB70bn (£7.8bn) over the next 10 years.
At its unveiling in Shanghai in December 2023, Xiaomi CEO Lei Jun said the company wants to become one of the world’s top five car makers within the next 15 to 20 years.
“Xiaomi will rival Porsche and Tesla, and create a dream car for the new era of the automotive industry,” he said.
Further Xiaomi models will include an SUV, according to plans already revealed by the Beijing-based company.
The basis for Xiaomi’s first production model is a new electric car platform that goes under the internal name Modena. It has been conceived to support 400-volt and 800-volt electric architectures, plus single- and dual-motor drivetrains.
The styling of the SU7 was developed in-house under the leadership of Xiaomi’s head of design, Sawyer Li. Li has contributed to several recent new cars, including the BMW iX and Circular Vision Concept during a five-year stint at the German car maker.
At 4997mm in length, 1963mm in width and 1440mm in height, the new saloon is 34mm longer, 3mm narrower and 44mm higher than the Porsche Taycan, and has a wheelbase 100mm longer than its German rival at 3000mm.
The sleek lines contribute to a claimed drag co-efficient of just 0.195. This makes it one of the most aerodynamically efficient production cars yet, beating the 0.199 claimed by Geely for the new Galaxy E5 and roughly matching GAC’s Hyper GT.
As well as being highly aerodynamic, Xiaomi also claims the SU7 boasts high levels of structural integrity. The rear body structure is cast in a 9100-tonne die-casting machine.
Power for the SU7 comes from Xiaomi’s in-house developed electric motors, named after combustion engine arrangements: the V6, V6s and V8s.
The base V6 develops 295bhp and 295lb ft of torque. It is planned to be used exclusively with a 400-volt electric architecture in price-leading variants of the SU7. The mid-range V6s gains an additional 74bhp and 74lb ft and is compatible with an 800-volt electric architecture.
Both the V6 and V6s operate at up to 21,000rpm, according to Xiaomi.
The dual-motor SU7 model uses a combination of the V6 and V6s motors for an overall output of 664bhp and a claimed 0-62mph time of 2.78sec. It is also equipped with an 875-volt charging system for ultra-rapid top-ups.
Due out in 2025, the V8s or so-called 'HyperEngine' is claimed to produce up to 670bhp and 468lb ft at a maximum efficiency of 98.11% and a power density of 10.14kW/kg operating on an 800-volt architecture. It can operate at speeds of up to 27,200rpm, according to Lei.
The Xiaomi CEO revealed prototype versions of the new Xiaomi motor have achieved up to 35,000rpm in testing, setting the scene for even more powerful iterations of the Chinese company’s new saloon in the future.
Initial SU7 models will feature a CATL-supplied lithium-ion battery with an energy capacity of 101kWh and a range of more than 497 miles. The battery uses cell-to-body construction with 14 layers of protection.
Lei says the SU7 can gain up to 137 miles of range from a five-minute charge and 317 miles on a 15-minute charge.
Xiaomi has also developed a 132kWh battery and a range of more than 620 miles on the Chinese light-duty vehicle test cycle (CLTC). The Modena platform used by the new Xiaomi model is said to be capable of accommodating a 150kWh version of battery for a range of 746 miles.
Pilot production of the SU7 has already begun at Xiaomi’s factory in Beijing.
Xiaomi was founded in 2010 by Lei Jun. It became China’s largest seller of smartphones in 2014, both under the Xiaomi and RedMi brands. Its products were initially sold exclusively through online shops.
However, it has since opened traditional sale centres to fuel its growth. In 2023, Xiaomi commanded some 12 per cent of worldwide smartphone sales. It is also a major manufacturer of electric home appliances.
Related News