How Nissan Builds Its e-Power Hybrid System That Drives Like an EV

Key Points
- Nissan’s e-Power uses an engine solely as a generator; electric motor drives the wheels.
- Production combines automated and manual assembly, followed by rigorous quality inspections.
- Oppama Plant closes March 2028; Rogue will debut e-Power in U.S. models for 2027.
A Unique Hybrid System
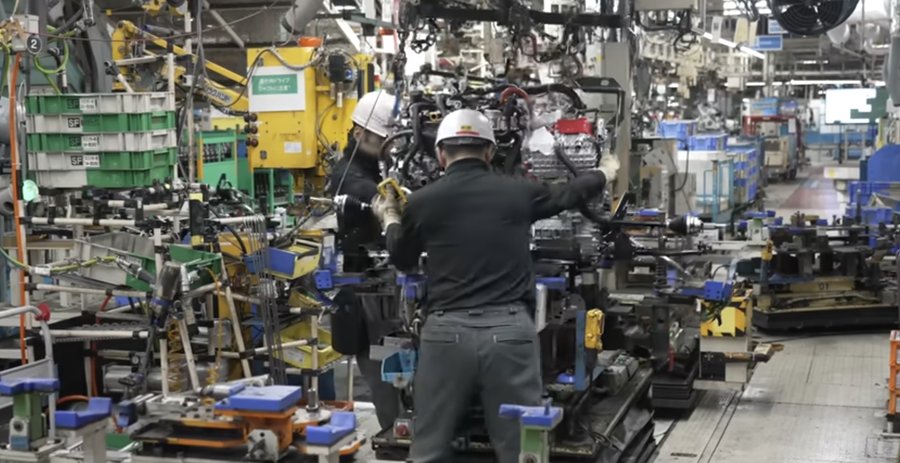
Nissan is approaching the growing electrified car market with the e-Power, which offers a different drivability compared to most hybrids. ProcessX shares on YouTube how this hybrid powertrain setup is made through behind-the-scenes footage at Nissan’s Yokohama Plant in Japan.
We Drove Nissan’s e-Power Hybrid and It Really Does Feel Like an EV Without the Hassle
Millions of Americans say they’re interested in EVs – but not quite ready to make the leap. If that describes you, Nissan may have the right alternative coming in 2026. After a long delay, the Japanese automaker is ready to introduce its new E-Power system into the U.S. market with the launch of the next-generation Nissan Rogue. What’s E-Power? And what’s it like to drive? Here’s what we discovered.
Paul Eisenstein
What makes e-Power different? The powertrain setup uses an engine solely as a generator, meaning an electric motor drives the wheels. As a result, e-Power cars drive like electric vehicles, providing instant torque and smooth operation. The engine will kick in at some point, usually when recharging or when the throttle demand is significant.
Nissan’s e-Power is a series hybrid, with the cutesy BMW i3 REx among the select few mass-market cars using this setup. Honda’s e:HEV system, while often mistaken for the same layout, only operates in series mode part of the time before allowing the engine to directly drive the wheels at speed. Despite legacy brands like Honda sticking to that traditional hybrid system, Nissan explained that engine vibrations and adding a multi-gear transmission aren’t worth adopting that approach.
At the Yokohama Plant, the coil-winding process for the stator is handled with a mix of automated machinery and manual work. Workers then perform the manual assembly of the glass tube before aligning the coil bundles with each electric circuit. The stator is then placed into its housing, followed by the rotor — the component that spins in response to the stator’s magnetic field — which completes the motor’s core assembly.
Likewise, much of the combustion-engine manufacturing is automated, from piston assembly to mounting the cylinder head onto the block. The Note uses a 1.2-liter three-cylinder engine, which powers the generator feeding the electric motor that produces 114 horsepower and 207 lb-ft of torque.
What’s Coming Next
Once completed, the e-Power units are transferred to the historic Oppama Plant, where Nissan performs full vehicle assembly. After assembly, each vehicle undergoes multiple quality inspections, including visual checks, performance verification, and water-intrusion testing.
Nissan, however, plans to cease operations at the Oppama Plant by March 2028 as part of its cost-cutting measures.
The Note and its e-Power system are not sold in the U.S., at least for now. The Rogue will be the first to receive the setup when its 2027 model arrives by the end of fiscal 2026. Nissan also offers a full EV with the Leaf, now in its third generation, introduced earlier this year.
Nouvelles connexes